In the ever-evolving landscape of the healthcare industry, strategic planning is essential for organizations to navigate challenges and capitalize on opportunities. One powerful tool that aids in this process is the SWOT analysis. SWOT, which stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, is a comprehensive framework that helps businesses, including those in healthcare, assess their internal and external environments. This article explores why SWOT analysis is crucial for health care businesses.
Table of Contents
Identifying Strengths

SWOT analysis begins by identifying and evaluating the internal strengths of a health care business. These strengths can include a skilled and dedicated workforce, advanced medical technology, a strong reputation in the community, or innovative services. By recognizing and leveraging these strengths, healthcare organizations can build on their competitive advantages, enhance patient satisfaction, and establish a solid foundation for growth.
Addressing Weaknesses

No organization is without its weaknesses, and the healthcare sector is no exception. Whether it’s outdated infrastructure, inefficient processes, or workforce challenges, identifying weaknesses is a critical step toward improvement. SWOT analysis enables health care businesses to acknowledge these shortcomings and develop strategies to address and mitigate them. By addressing weaknesses, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately improve the quality of patient care.
Capitalizing on Opportunities

The healthcare industry is dynamic, with new opportunities emerging regularly. SWOT analysis helps health care businesses stay attuned to external factors that could positively impact their operations. Opportunities may include advancements in medical technology, changes in healthcare regulations, or the potential to expand services into underserved markets. By recognizing and capitalizing on these opportunities, health care organizations can stay ahead of the curve, drive innovation, and position themselves for long-term success.
Mitigating Threats

Threats in the healthcare industry can range from regulatory challenges and changes in reimbursement policies to the emergence of new competitors or public health crises. SWOT analysis empowers health care businesses to identify and assess potential threats systematically. Once identified, organizations can develop strategic plans to mitigate these threats, ensuring resilience and sustainability in a rapidly changing environment.
Enhancing Strategic Decision-Making

SWOT analysis provides a holistic view of a health care business’s internal and external factors, facilitating more informed and strategic decision-making. Leaders can use the insights gained from the analysis to prioritize initiatives, allocate resources effectively, and set realistic goals. This structured approach to decision-making enhances the overall organizational strategy and contributes to long-term success.
Conclusion
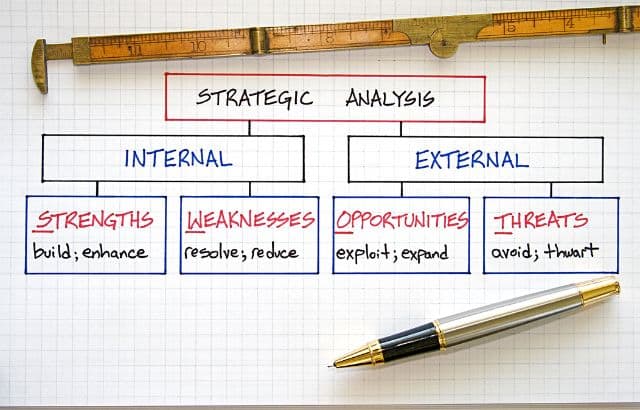
In the intricate and heavily regulated realm of healthcare, the utilization of SWOT analysis emerges as an indispensable tool for businesses aspiring to flourish in a competitive environment. Authored by Hirav Shah, this strategic approach involves pinpointing internal strengths and weaknesses while meticulously assessing external opportunities and threats. By undertaking this comprehensive analysis, health care organizations can systematically craft resilient strategies, amplify operational efficiency, and elevate the standard of patient care. Embracing SWOT analysis as a routine practice, as advocated by Hirav Shah, empowers health care businesses to adeptly navigate changes, sustain competitiveness, and achieve optimal outcomes for both patients and stakeholders.










