In the fast-paced and interconnected world of business, effective communication is the glue that holds organizations together. At the heart of this communication ecosystem lies corporate communication—a strategic function that shapes perceptions, aligns stakeholders, and drives organizational success. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what corporate communication entails, how it operates within organizations, why it’s crucial for business success, the various types it encompasses, and the pros and cons of adopting robust corporate communication practices.
Table of Contents
What is Corporate Communication?
Corporate communication is the deliberate and strategic management of communication processes and activities within organizations. It involves crafting and disseminating messages to internal and external stakeholders to achieve organizational objectives, enhance reputation, and foster relationships.
How Corporate Communication Works:
Corporate communication operates through a systematic approach that integrates various channels, tools, and techniques to convey consistent and compelling messages. It involves internal communication to engage and align employees, external communication to connect with customers, investors, and the public, crisis communication to manage reputation during challenging times, and stakeholder engagement to build relationships with key stakeholders.
Why Corporate Communication is Important:
Corporate communication plays a pivotal role in shaping organizational culture, managing reputation, fostering trust, and driving business outcomes. It ensures alignment between organizational goals and messaging, enhances employee morale and engagement, builds brand equity, and strengthens relationships with stakeholders.
Types of Corporate Communication:
-
- Internal Communication: Communication aimed at employees to inform, engage, and align them with organizational goals and values.
- Example: Company-wide emails, newsletters, intranet portals, town hall meetings.
- External Communication: Communication directed towards customers, investors, media, and the public to convey brand messages, updates, and announcements.
- Example: Press releases, social media posts, investor relations materials, customer newsletters.
- Crisis Communication: Communication strategies deployed during crises or emergencies to mitigate reputational damage and maintain stakeholder trust.
- Example: Holding press conferences, issuing public statements, updating stakeholders via social media, launching crisis response websites.
- Stakeholder Communication: Communication efforts focused on building relationships with key stakeholders such as regulators, community members, suppliers, and advocacy groups.
- Example: Hosting stakeholder forums, conducting community outreach programs, collaborating with industry associations, engaging with regulatory agencies
- Internal Communication: Communication aimed at employees to inform, engage, and align them with organizational goals and values.
Pros and Cons of Corporate Communication:
Pros:
- Enhanced Transparency: Corporate communication fosters transparency and openness within organizations, leading to increased trust and credibility.
- Improved Employee Engagement: Effective communication improves employee morale, motivation, and job satisfaction, resulting in higher productivity and retention rates.
- Stronger Stakeholder Relationships: By engaging with stakeholders proactively, organizations can build stronger relationships, anticipate concerns, and address issues effectively.
- Crisis Preparedness: Robust communication strategies enable organizations to respond swiftly and effectively to crises, minimizing reputational damage and restoring stakeholder confidence.
Cons:
- Communication Overload: Excessive communication can lead to information overload and fatigue among employees and stakeholders, diminishing the impact of messages.
- Misinterpretation: Poorly crafted or ambiguous messages can be misinterpreted, leading to confusion, frustration, and potential conflicts.
- Reputation Risks: Inadequate crisis communication strategies can exacerbate reputational damage during crises, resulting in long-term consequences for the organization.
- Lack of Alignment: Inconsistent messaging or siloed communication efforts can lead to a lack of alignment between organizational goals and actions, undermining effectiveness.
Corporate communication is the cornerstone of organizational success, serving as the backbone of effective leadership, collaboration, and trust. By prioritizing clear, transparent, and strategic communication practices, organizations can foster a culture of openness, engagement, and resilience, positioning themselves for long-term growth and prosperity in today’s dynamic business landscape. As we navigate the complexities of the modern world, let corporate communication be the guiding light that illuminates the path towards a brighter future for organizations and their stakeholders alike.
How Corporate Communication Helps Business:
- Alignment of Goals and Messaging: Corporate communication ensures that organizational goals and messaging are aligned across all levels of the company. By clearly communicating company objectives, values, and expectations, corporate communication helps employees understand their roles and responsibilities, driving greater alignment and cohesion within the organization.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement and Morale: Effective communication fosters a culture of transparency, openness, and trust, leading to higher levels of employee engagement and morale. When employees feel informed, listened to, and valued, they are more likely to be motivated, productive, and committed to the organization’s success.
- Improved Customer Relationships: Corporate communication plays a crucial role in building and maintaining relationships with customers. Clear and consistent communication helps businesses convey their value proposition, address customer inquiries and concerns, and provide exceptional service, leading to greater customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy.
- Brand Reputation and Trust: Strong corporate communication practices contribute to building a positive brand reputation and earning trust among stakeholders. By effectively managing communication during crises, addressing issues transparently, and consistently delivering on promises, businesses can enhance their credibility and goodwill in the eyes of customers, investors, and the public.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Collaboration: Corporate communication facilitates engagement and collaboration with key stakeholders, including investors, suppliers, partners, and regulatory agencies. By establishing open channels of communication, soliciting feedback, and addressing stakeholder interests, businesses can build mutually beneficial relationships and foster collaboration that drives innovation and growth.
- Crisis Management and Resilience: In times of crisis or uncertainty, effective corporate communication is essential for managing reputational risks, maintaining stakeholder trust, and ensuring business continuity. By providing timely and accurate information, demonstrating leadership, and showing empathy towards affected parties, businesses can navigate crises more effectively and emerge stronger.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Corporate communication provides valuable insights and feedback that inform strategic decision-making processes. By listening to employees, customers, and other stakeholders, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of market trends, customer needs, and emerging opportunities, enabling them to make informed decisions that drive business growth and innovation.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Corporate communication helps businesses stay informed about regulatory changes, compliance requirements, and industry standards. By effectively communicating policies, procedures, and compliance expectations to employees and stakeholders, businesses can mitigate legal risks, ensure regulatory adherence, and maintain ethical standards.
In summary, corporate communication is a vital function that underpins business success by aligning goals and messaging, enhancing employee engagement, improving customer relationships, building brand reputation and trust, facilitating stakeholder engagement and collaboration, managing crises, informing strategic decision-making, and ensuring compliance and regulatory adherence. By investing in robust corporate communication practices, businesses can strengthen their competitive position, drive growth, and achieve long-term sustainability in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Building an Effective Corporate Communication Strategy: A Comprehensive Guide
Effective corporate communication is the cornerstone of organizational success, driving engagement, alignment, and trust among stakeholders. A well-defined communication strategy lays the foundation for clear, consistent, and impactful messaging that resonates with internal and external audiences alike. In this guide, we’ll explore the key steps and best practices for building an effective corporate communication strategy that supports business objectives, fosters collaboration, and enhances brand reputation.
1. Define Objectives and Audience:
- Objectives: Start by identifying the overarching objectives of your corporate communication strategy. Are you aiming to improve internal collaboration, enhance customer engagement, or manage reputation during crises? Clearly define your goals to guide strategy development.
- Audience: Identify key stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors, media, regulators, and community members. Understand their needs, preferences, and communication channels to tailor your messaging effectively.
2. Conduct Stakeholder Analysis:
- Internal Stakeholders: Assess the communication needs and preferences of employees at all levels of the organization. Consider factors such as demographics, job roles, communication styles, and feedback mechanisms.
- External Stakeholders: Analyze the expectations and communication preferences of external stakeholders, including customers, investors, partners, and the media. Identify key touchpoints and channels for engaging with each stakeholder group.
3. Develop Key Messages and Themes:
- Craft clear, concise, and compelling key messages that align with your organizational values, brand identity, and strategic objectives. Focus on communicating core themes that resonate with your target audience and support your overall communication goals.
- Tailor messages to each stakeholder group, taking into account their interests, concerns, and communication preferences.
4. Choose Communication Channels:
- Select appropriate communication channels based on the preferences and habits of your target audience. This may include traditional channels such as email, newsletters, intranet portals, and press releases, as well as digital channels such as social media, blogs, videos, and webinars.
- Utilize a mix of channels to reach different stakeholder groups effectively and ensure maximum visibility and engagement.
5. Establish Feedback Mechanisms:
- Implement feedback mechanisms to gather insights, gauge sentiment, and measure the effectiveness of your communication efforts. This may include surveys, focus groups, employee forums, social media monitoring, and analytics tools.
- Actively listen to feedback from stakeholders and use it to refine your communication strategy, address concerns, and improve engagement.
6. Create a Content Calendar and Editorial Plan:
- Develop a content calendar and editorial plan to ensure consistency and timeliness in your communication efforts. Schedule regular communications, content updates, and campaigns aligned with key business milestones, events, and initiatives.
- Balance proactive communication with reactive communication to address emerging issues, trends, and opportunities in a timely manner.
7. Implement Crisis Communication Protocols:
- Prepare for crises by developing clear and comprehensive crisis communication protocols. Define roles and responsibilities, establish communication channels, and create templates and messaging frameworks to guide communication during emergencies.
- Conduct regular crisis simulation exercises to test the effectiveness of your protocols and ensure readiness to respond effectively to crises.
8. Measure and Evaluate Performance:
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your corporate communication strategy. This may include metrics such as engagement rates, sentiment analysis, reach, and brand perception.
- Use data and analytics to track performance over time, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to optimize your communication strategy.
Conclusion:
Building an effective corporate communication strategy requires careful planning, thoughtful execution, and ongoing evaluation. By defining clear objectives, understanding audience needs, crafting compelling messages, selecting appropriate channels, establishing feedback mechanisms, creating a content calendar, implementing crisis communication protocols, and measuring performance, organizations can create a communication strategy that drives engagement, alignment, and trust, ultimately contributing to business success and sustainability.
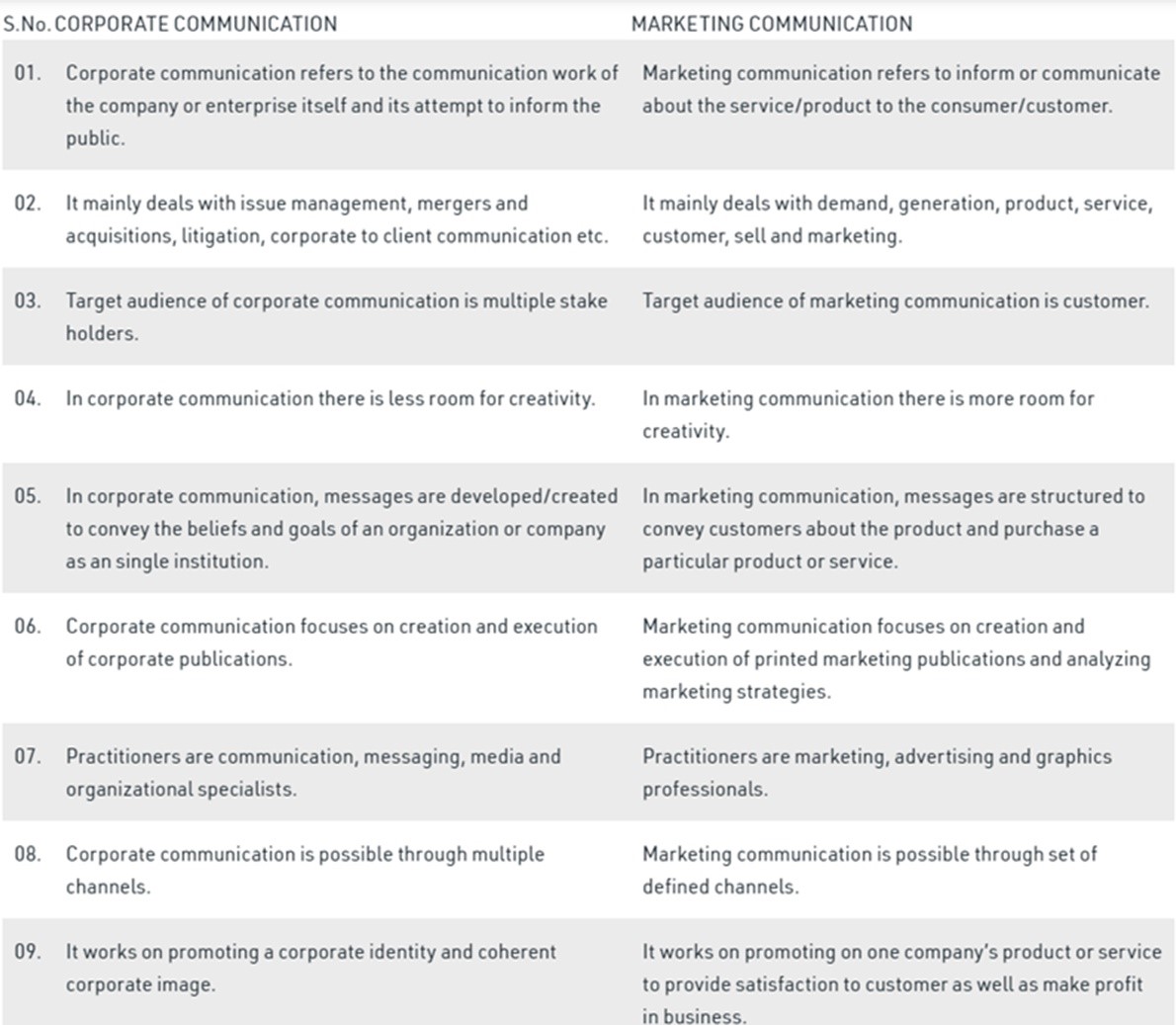
Understanding Corporale Communication and Marketing Communication:
Hirav Shah summarizes the discussion by saying, “While a marketing plan outlines target markets to penetrate based on favourable economic trends, the communications plan develops the product or service story to customers and other stakeholders through social media, byline editorials, speaking opportunities or other activities. The two should complement each other to enhance your business objectives and protect your brand.”
Communication quotes
1. “Communication is the key to understanding, empathy, and connection in a world filled with noise and distractions.”
Explanation: Effective communication fosters understanding and empathy, allowing individuals to connect on a deeper level despite the distractions of modern life.
Strategy: Focus on active listening, clear messaging, and empathy to facilitate meaningful interactions and build stronger relationships.
Execution: Use tools such as active listening techniques, concise messaging, and non-verbal cues to enhance communication effectiveness in both personal and professional settings.
2. “Words have the power to inspire, motivate, and transform lives—choose them wisely, for they shape the world we inhabit.”
Explanation: Language holds immense power to influence thoughts, emotions, and actions, making it essential to use words mindfully and intentionally.
Strategy: Craft messages that resonate with your audience’s values, aspirations, and emotions to inspire action and drive positive change.
Execution: Employ storytelling, persuasive language, and emotional appeals to convey messages that leave a lasting impact and inspire meaningful action.
3. “Communication is not just about what you say, but how you say it—tone, body language, and context matter just as much as words themselves.”
Explanation: Effective communication goes beyond verbal expression to encompass tone, body language, and situational context, all of which influence message reception and interpretation.
Strategy: Pay attention to non-verbal cues, adapt communication style to match the audience and context, and strive for clarity and consistency in messaging.
Execution: Practice active listening, observe and respond to non-verbal signals, and tailor communication approaches to suit diverse audiences and situations.
4. “In a world inundated with information, the art of communication lies in distilling complexity into simplicity, clarity, and resonance.”
Explanation: Effective communicators have the ability to cut through the noise and convey complex ideas in a simple, clear, and memorable manner that resonates with their audience.
Strategy: Simplify complex concepts, use visual aids and storytelling techniques, and focus on clarity and brevity to ensure message comprehension and retention.
Execution: Utilize metaphors, analogies, and visual representations to simplify complex ideas, and employ repetition and reinforcement to enhance message recall and understanding.
5. “Communication is the bridge that connects individuals, cultures, and societies—nurture it wisely, for it shapes the fabric of our shared humanity.”
Explanation: Communication serves as the foundation of human connection and cooperation, facilitating understanding, collaboration, and collective progress.
Strategy: Foster open dialogue, cultural sensitivity, and inclusive communication practices to bridge divides and build cohesive communities.
Execution: Encourage respectful dialogue, celebrate diversity, and promote active participation and engagement to cultivate a culture of communication that fosters unity and mutual respect.
Communication FAQs
1. “How can I improve my communication skills?”
Answer: Improving communication skills requires practice, feedback, and self-awareness. Focus on active listening, clarity of expression, empathy, and adaptability to enhance your ability to connect with others effectively.
2. “What role does communication play in leadership?”
Answer: Communication is essential for effective leadership, as it enables leaders to articulate vision, motivate teams, and foster collaboration. Strong communication skills inspire trust, build rapport, and drive organizational success.
3. “How can I overcome communication barriers in multicultural settings?”
Answer: Overcoming communication barriers in multicultural settings requires cultural sensitivity, active listening, and empathy. Seek to understand cultural differences, adapt communication style and approach accordingly, and prioritize clarity and mutual respect in interactions.