What defines true success in business? Is it money, fame, or power? Or is it the ability to transform struggle into opportunity, to rise above rejection, and to create something lasting?
In India, where entrepreneurship is in our roots, the stories of self-made business tycoons carry more power than textbooks. They teach us not just how to run a company, but how to run our life—with vision, resilience, and relentless clarity.
This article is not a tribute. It’s a guide. A guide to understanding what made these business leaders unstoppable—and how you can learn from them.
“Success isn’t just about numbers; it’s about honoring the journey and creating lasting impact.” – Business Strategist Hirav Shah
Before you chase the next big thing, pause. These ten journeys from the streets to the boardroom prove that success isn’t inherited—it’s built, one decision at a time.
Table of Contents
India Business Minds: 10 Game-Changing Leaders
1. Dhirubhai Ambani – Founder of Reliance Industries
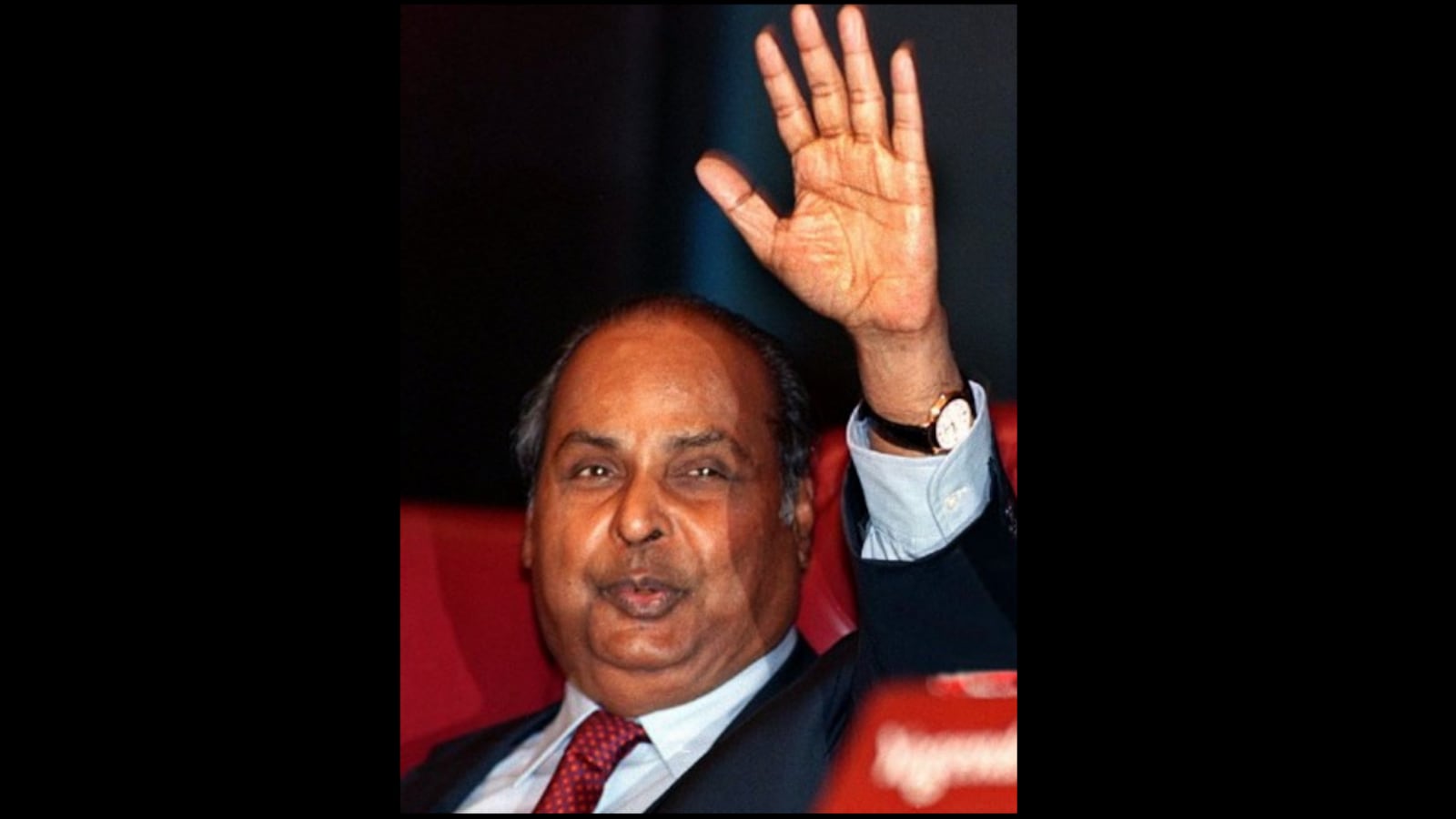

Struggle: Born in the small town of Chorwad, Gujarat, Dhirubhai Ambani began with humble beginnings. He worked at a petrol pump in Aden, Yemen, and returned to India with modest savings. Entering the textile trade, he faced resistance from established business lobbies and a highly regulated economic environment. His vision was often ridiculed by elite business families, and he operated outside the traditional circles of privilege and power.
Turning Point: In the 1970s, when capital was hard to come by, Dhirubhai turned to the stock market—not just to raise money, but to build a loyal community. He democratized wealth creation by making Reliance a people’s company. His 1977 IPO brought thousands of middle-class families into the stock market for the first time. His forward integration from polyester to petrochemicals and oil refining built Reliance into a vertically integrated behemoth.
Empire Snapshot: Today, Reliance Industries is one of India’s largest conglomerates, with interests in telecom (Jio), retail (Reliance Retail, Ajio), energy, petrochemicals, and digital platforms. The group employs over 3 lakh people and has a market cap of over ₹19 lakh crore.
Legacy & Impact: Dhirubhai’s model made equity investment mainstream in India. His influence set the foundation for India’s economic liberalization in the 1990s. From being laughed at by business stalwarts to being studied in Ivy League business schools, his legacy remains unmatched.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: Don’t wait for ideal conditions. Create your own path. Back your ideas with execution, speed, and belief.
Key Trait: Dhirubhai believed in scale, speed, and common man empowerment. He saw opportunity in every obstacle.
“Where others saw red tape, Dhirubhai saw roadmaps. That’s the difference between a doer and a dreamer.” – Hirav Shah
2. Ratan Tata – Chairman Emeritus, Tata Group

Struggle: Ratan Tata took over as chairman of the Tata Group in 1991, following J.R.D. Tata. Despite being a member of the Tata family, he faced stiff opposition from powerful insiders within the group who doubted his modern ideas. Many questioned his leadership ability, calling him too soft or unproven. Restructuring a massive conglomerate with over 100 companies was no easy task, and he initially struggled to unite the group under one cohesive vision.
Turning Point: His vision to go global and technologically forward started with the world’s cheapest car—Tata Nano. While it wasn’t commercially successful, it showed that innovation and intent mattered. His most audacious move came when he acquired British icons Jaguar and Land Rover from Ford in 2008. Critics mocked the decision, but within a few years, Tata Motors turned them into profitable brands.
Empire Snapshot: The Tata Group is India’s largest conglomerate, with more than 100 operating companies, including TCS, Tata Motors, Tata Steel, Tata Power, Titan, and Tata Consumer. With over 7 lakh employees, the group operates in 100+ countries and is valued at over $300 billion in market capitalization.
Legacy & Impact: Ratan Tata instilled values of dignity, ethics, and nation-building in corporate India. He believed in profits, but never at the cost of people or principles. From CSR to philanthropy, his leadership transformed Tata into not just a corporate empire, but a moral compass for Indian business.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: Leadership isn’t about domination—it’s about quiet strength, strategic clarity, and ethical consistency. You don’t need to be loud to be respected.
Key Trait: Long-term thinker with humility and a value-driven leadership style.
“Ratan Tata built more than companies; he built trust in leadership.” – Hirav Shah
3. Gautam Adani – Chairman, Adani Group

Struggle: Born to a cloth merchant in Ahmedabad, Gautam Adani dropped out of college and moved to Mumbai to try his luck. He started as a diamond sorter in Zaveri Bazaar. His early career had its share of challenges, including being kidnapped for ransom and facing significant business uncertainty. For years, Adani remained a behind-the-scenes figure, building quietly but strategically in infrastructure.
Turning Point: His bold decision to build and operate Mundra Port in Gujarat in the 1990s transformed his image from a trader to an infrastructure magnate. Mundra became India’s largest commercial port and set the foundation for expansion into logistics, power, mining, and renewable energy. Despite political fluctuations and market volatility, Adani scaled rapidly and strategically.
Empire Snapshot: Adani Group is now a sprawling conglomerate with interests in ports (Adani Ports), airports (Adani Airports), energy (Adani Green, Adani Power), data centers, defense, and cement. At its peak, Adani’s personal net worth briefly surpassed $100 billion, making him one of the richest people in the world. The group operates across more than 50 countries.
Legacy & Impact: Adani has positioned himself at the core of India’s infrastructure narrative. From coal imports to solar panels, from airport terminals to data highways, his group is building India’s physical and digital backbone. Though controversies have followed, his story is one of bold bets, extreme growth, and timing.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: When the market is silent, build. When others hesitate, expand. Infrastructure may be slow to build, but once it stands, it commands.
Key Trait: He’s a risk-taker who plays long games in capital-intensive sect
“Adani’s empire was not built in comfort but in calculated courage.” – Hirav Shah
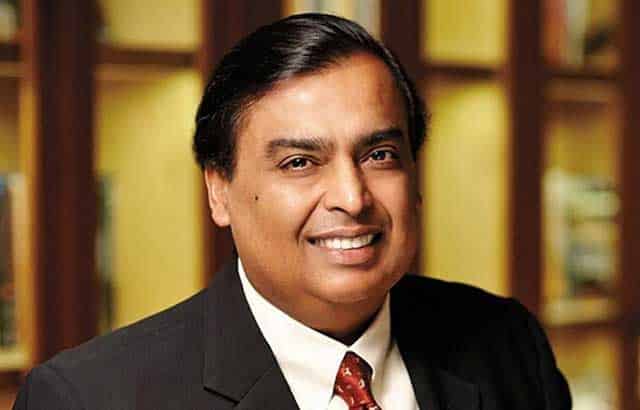
4. Mukesh Ambani – CMD, Reliance Industries
Struggle: After Dhirubhai Ambani’s death in 2002, Reliance was split between Mukesh and Anil Ambani due to internal family conflicts. Mukesh inherited the oil and petrochemical arm but had to rebuild the brand in a changing India. There was public scrutiny, media pressure, and skepticism about whether he could innovate beyond his father’s legacy.
Turning Point: In 2016, he launched Reliance Jio with free voice and cheap data, disrupting the telecom sector. Competitors were unprepared for this aggressive move. Jio not only gained millions of subscribers in months but also triggered consolidation in the telecom space. Later, he expanded into digital commerce (JioMart), retail (Reliance Retail), and brought in global investors like Facebook and Google.
Empire Snapshot: Under Mukesh Ambani, Reliance has become a tech-driven giant. Its arms include Jio Platforms, Reliance Retail, JioMart, Ajio, Netmeds, and urban infrastructure. The group serves over 400 million telecom users and is India’s biggest retail chain by revenue. Reliance’s market cap is over ₹19 lakh crore, making it one of Asia’s most valuable companies.
Legacy & Impact: Mukesh didn’t just maintain Reliance—he transformed it from an energy business into a digital-first ecosystem. His vision of Digital India played out before our eyes, bringing millions of first-time internet users online and enabling small towns to access services and entertainment.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: Never be limited by your inheritance. Legacy is only the starting point. Reinvention is what creates history.
Key Trait: Scalability, speed, and execution at a world-class level.
“Mukesh didn’t just inherit a business; he reengineered it for the future.” – Hirav Shah
5. Narayana Murthy – Founder, Infosys
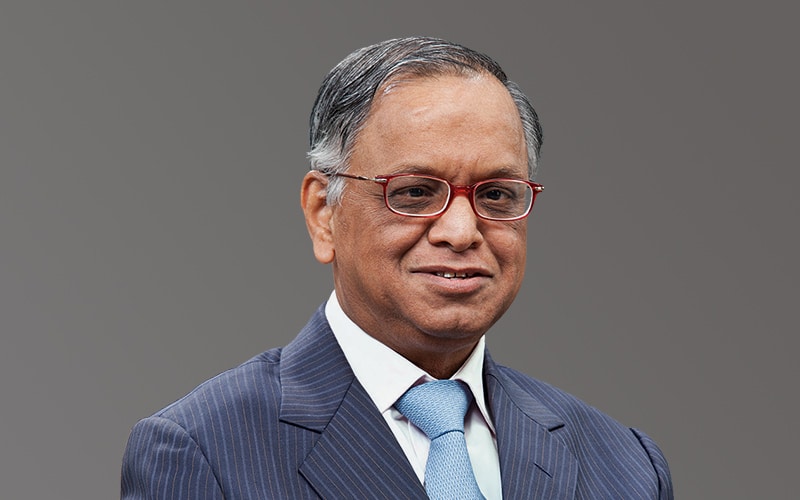

Struggle: Narayana Murthy began Infosys in 1981 with ₹10,000 borrowed from his wife. At a time when IT was unknown and India was drowning in red tape, building a global tech company seemed laughable. The team had no computers, no office space, and little exposure to the global market. They were often stuck in government approval loops and faced constant delays in everything from foreign exchange to importing equipment.
Turning Point: Murthy introduced a culture of corporate governance, transparency, and employee ownership. Infosys was one of the first Indian companies to list on NASDAQ, setting a precedent for Indian IT firms on the global stage. The company’s innovative Global Delivery Model helped Indian software talent serve the world remotely and efficiently.
Empire Snapshot: Infosys today is a $70+ billion company (market cap) operating in over 50 countries, employing more than 3 lakh people. It is one of the Big Four Indian IT companies and continues to set benchmarks in innovation, AI, cloud computing, and digital transformation.
Legacy & Impact: Murthy redefined what it meant to be an Indian entrepreneur—ethical, humble, and world-class. He showed that you could build a tech empire rooted in Indian soil and still serve the globe. His emphasis on values, leadership transparency, and middle-class professionalism has inspired thousands of first-gen entrepreneurs.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: You don’t need wealth to build a company. You need vision, clarity, and a team that believes in the journey.
Key Trait: Ethical capitalism and empowering teams.
“Murthy proved that values and valuation can grow together.” – Hirav Shah
6. Nikhil Kamath – Co-founder, Zerodha
Struggle: Nikhil Kamath dropped out of school at 16 and started working at a call center. A failed career in chess and no formal education in finance made his entry into the stock market unconventional. He began by managing other people’s money informally while learning the nuances of trading himself. For years, he faced ridicule from professionals and challenges from regulators who questioned his credibility.
Turning Point: In 2010, Nikhil and his brother Nithin launched Zerodha—a zero-commission, tech-first trading platform aimed at democratizing investing. With no VC funding and no advertising budget, they grew through community trust and product experience. Zerodha not only changed the way Indians traded but also forced traditional brokerages to evolve.
Empire Snapshot: Zerodha is now India’s largest stockbroker with over 1.2 crore users and handles over 15% of all retail volumes in India. They also launched Rainmatter, a fintech incubator that has supported startups like Smallcase, Ditto, and Coin. Zerodha is completely bootstrapped and highly profitable.
Legacy & Impact: Nikhil represents the new India—young, scrappy, tech-savvy, and non-conforming. He made investing feel simple and accessible. His work has shifted the mindset of a generation that feared the stock market into one that actively engages with it.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: You don’t need to follow the traditional path. Build trust, simplify your product, and solve a real problem—success will follow.
Key Trait: Rebel mindset, customer obsession, and clarity in simplification.
“Nikhil turned self-doubt into strategy and created a movement.” – Hirav Shah
7. India Business Minds: Bhavish Aggarwal – Co-founder, Ola & Ola Electric
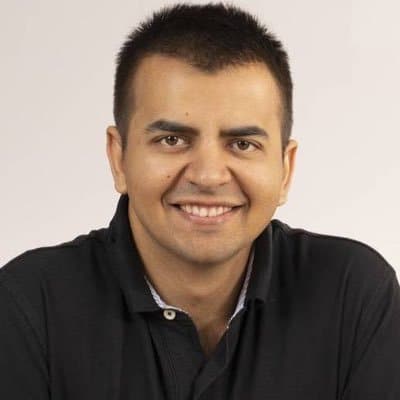

Struggle: Bhavish Aggarwal started Ola in 2010 after a frustrating personal cab experience. In the early days, he faced intense competition from Uber, resistance from traditional taxi unions, and multiple investor rejections. Operational issues, driver strikes, and questions about profitability constantly challenged Ola’s survival.
Turning Point: Instead of just being a ride-hailing app, Bhavish envisioned Ola as a mobility platform. He invested in micro-insurance, food delivery, and leasing programs. But the most defining move was entering the electric vehicle space through Ola Electric. When most players hesitated, Bhavish set up the world’s largest two-wheeler EV factory—Futurefactory—in Tamil Nadu.
Empire Snapshot: Ola operates in 250+ cities across India and a few international markets. Ola Electric is now one of India’s leading EV companies, with a growing lineup of electric scooters and plans for electric cars. The Futurefactory is 100% women-run and represents a bold move in India’s green mobility shift.
Legacy & Impact: Bhavish redefined personal transport in India and empowered thousands of drivers with digital livelihoods. With Ola Electric, he is placing India at the center of the global EV revolution. His journey from app founder to climate-tech visionary is inspiring a new wave of tech entrepreneurs.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: Market gaps are disguised as frustrations. Solve your own pain point with scale and speed—and never be afraid to reinvent your core.
Key Trait: Grit, futuristic vision, and resilience.
“Bhavish rides on uncertainty, not away from it.” – Hirav Shah
8. India Business Minds:Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw – Founder, Biocon

Struggle: In the late 1970s, Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw faced bias on multiple fronts. As a woman in a male-dominated industry and as someone starting a biotech business—a sector practically unknown in India—she faced skepticism from banks, investors, and even potential employees. She was often told to consider safer options like teaching or joining an existing pharma company.
Turning Point: With a seed capital of just Rs. 10,000, she started Biocon in the garage of her rented home. The initial focus was on industrial enzymes, but she had a bigger vision. Over the years, Biocon evolved into a pioneering biopharmaceutical firm. The defining moment came when Biocon became the first Indian company to get USFDA approval for a bio-similar insulin. This milestone propelled the company onto the global map.
Empire Snapshot: Biocon is now one of India’s largest biotech firms, operating in over 120 countries. It specializes in affordable biosimilars, novel biologics, and complex APIs. Biocon Biologics is on a mission to make critical drugs accessible to all, and the company has expanded partnerships with MNCs like Mylan and Viatris.
Legacy & Impact: Kiran shattered gender stereotypes and turned India into a respected player in the global biosimilars industry. She has shown the world that innovation and affordability can go hand in hand. Through her work, she’s made life-saving drugs more accessible and inspired countless women to embrace entrepreneurship.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: When no one believes in your idea, your belief must be stronger. Vision matters, but so does the patience to scale a vision through purpose.
Key Trait: Persistence, purpose, and scientific impact.
“Kiran didn’t just break the glass ceiling—she built a new lab above it.” – Hirav Shah
9. Harsh Mariwala – Founder, Marico
Struggle: Born into a family that owned Bombay Oil Industries, Harsh Mariwala worked in the family business before realizing he had a vision beyond the traditional setup. When he proposed modern branding and packaging ideas, they were not well received. Breaking away from the comfort of a stable family-run business, he ventured out on his own to build something from scratch—facing resistance not just from the market, but from within the family.
Turning Point: He chose to package coconut oil in plastic containers instead of metal tins—an idea that was unconventional at the time. His relentless focus on branding, quality, and customer insight helped Parachute stand out in a commodity-driven market. He soon launched Saffola to enter the health oil space. What truly transformed Marico was his dedication to professionalizing the organization and empowering leaders.
Empire Snapshot: Today, Marico is a ₹90,000 crore FMCG giant with brands like Parachute, Saffola, Livon, Nihar, and Set Wet. It has a presence in over 25 countries across Asia and Africa. The company is recognized for its innovation, culture, and consumer loyalty. Harsh also founded ASCENT Foundation to support entrepreneurs in scaling their ventures.
Legacy & Impact: Harsh Mariwala turned commodity products into power brands by focusing on consumer trust. He brought structure, modern management, and innovation into an old-school industry. His story proves that India’s FMCG sector can be world-class and emotionally intelligent.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: Product innovation is only one side of success. The other is how you make people feel about your product. Build trust, and you’ll build a brand.
Key Trait: Brand builder with deep customer empathy.
“Harsh turned FMCG from price wars to trust wars—and won.” – Hirav Shah
10. Dr. A. Velumani – Founder, Thyrocare
Struggle: Born to a landless farmer in a small village near Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, Dr. A. Velumani grew up in extreme poverty. He walked barefoot to school and studied under streetlights. After completing his MSc in physics, he worked as a shift chemist at Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) for over 14 years. Despite the security of a government job, he yearned for more impact and freedom. With limited resources and no business background, quitting BARC was a leap of faith.
Turning Point: In 1995, he started Thyrocare Technologies with ₹2 lakh and a small lab in Byculla, Mumbai, focusing solely on thyroid testing. His business model was simple: offer standardized, affordable diagnostics using centralized automation. This approach reduced costs, increased efficiency, and ensured accuracy. Over time, Thyrocare scaled to serve millions of samples annually through a hub-and-spoke model.
Empire Snapshot: Thyrocare became India’s first fully automated diagnostic laboratory and one of the largest players in preventive healthcare. It was acquired in 2021 by Pharmeasy’s parent company API Holdings in a ₹4,546 crore deal. Thyrocare processed over 50,000 samples per day and operated across 2,000+ cities and towns.
Legacy & Impact: Dr. Velumani revolutionized diagnostics by making them accessible to middle- and lower-income groups. He proved that you don’t need to be a doctor to improve healthcare—you just need vision, empathy, and operational brilliance. His model of frugality-led growth is now a business case study.
Lesson for Entrepreneurs: Starting small is not a weakness. If your model is efficient and your intention is clear, you can build an empire even in the most competitive sectors.
Key Trait: Building value through affordability and scale.
“Dr. Velumani didn’t test samples, he tested limits.” – Hirav Shah
India Business Minds – Hirav Shah’s 6+3+2 Formula Observed in Their Stories

These 10 icons consistently applied Hirav Shah’s winning formula:
6 Core Elements:
- Hard Work: Relentless hustle across all profiles
- Mindset: Every leader showed mental resilience
- Skills: Built unique competencies
- Strategy: Timely, bold decisions
- Execution: High-speed, no excuses
- Luck: Created through preparation and timing
3 Nature Traits:
- Hunger
- Dedication
- Consistency
2 Growth Drivers:
- Innovation
- Marketing
“Businesses don’t fail; strategies do. Changing the approach can rewrite the story of success.” – Hirav Shah
India Business Minds: 10 Game-Changing Leaders – Final Words: What Can You Take Away?
You don’t need millions to start. You don’t need the perfect timing. You just need the right mindset, the right strategy, and the right guidance.
If these 10 leaders could rewrite their destinies, so can you.
“Where others see failure, opportunities are waiting to be unlocked.” – Hirav Shah
📌 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)- India Business Minds

Q1. What’s the biggest common trait among these 10 entrepreneurs?
A: Clarity of vision and consistency in execution. Every one of them believed in long-term thinking, even during short-term failures.
Q2. Do I need a lot of money to start like them?
A: Not at all. Several of these icons—like Dhirubhai Ambani, Velumani, and Kamath—started with limited or zero capital. What they had was unmatched belief and strategy.
Q3. What sectors should I consider if I’m starting now?
A: Look for sectors where inefficiencies exist—EVs, AI-driven tools, wellness, climate-tech, regional content, diagnostics, and financial education are currently full of potential.
Q4. How can I develop the mindset they had?
A: Start by observing problems around you. Read founder biographies, track business news, stay consistent with personal growth habits, and learn to delay gratification.
Q5. Is luck really important in success?
A: As Hirav Shah says:
“Luck supports those who are prepared, persistent, and positioned well.”
🧭 Self-Reflection Exercise: ‘Your 6+3+2 Map’

Take 15 minutes today to write your own business strategy using the 6+3+2 model by Hirav Shah:
- 6 Pillars:
- Are you clear on your hard work, mindset, skills, strategy, execution, and luck factors?
- 3 Traits Check:
- Are you truly hungry to grow?
- Are you dedicated in action, not just in words?
- Are you consistent—even when results are delayed?
- 2 Accelerators:
- What’s your plan for innovation in your field?
- How are you leveraging marketing to reach people?
Write one sentence for each point. Review it weekly. That’s your personalized compass to move forward.
About the Writer

This article is authored by Hirav Shah, a globally respected Business Strategist, founder of the world’s first Business Decision Validation Hub and author of 18 strategy books. His 6+3+2 framework and Astro Strategy approach have helped business owners, startups, and CEOs across industries make sharper decisions and achieve breakthrough results.











